Introduction
Patio heaters have become essential for extending the usability of outdoor spaces such as gardens, patios, restaurants, and cafés. Among the most common options available in the market are electric patio heaters and gas patio heaters. Each heating method has its own characteristics, advantages, and limitations, making the choice highly dependent on the user’s needs, environment, and budget. This article provides a comprehensive comparison between electric and gas patio heaters, examining their design, performance, efficiency, cost implications, installation requirements, and environmental impacts. By analyzing these aspects, readers can gain a clearer understanding of which heating system may be more suitable for different applications.
Design and Operating Principles
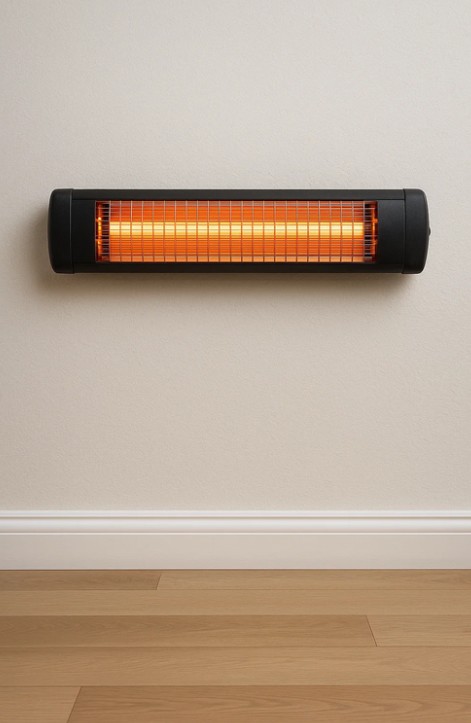
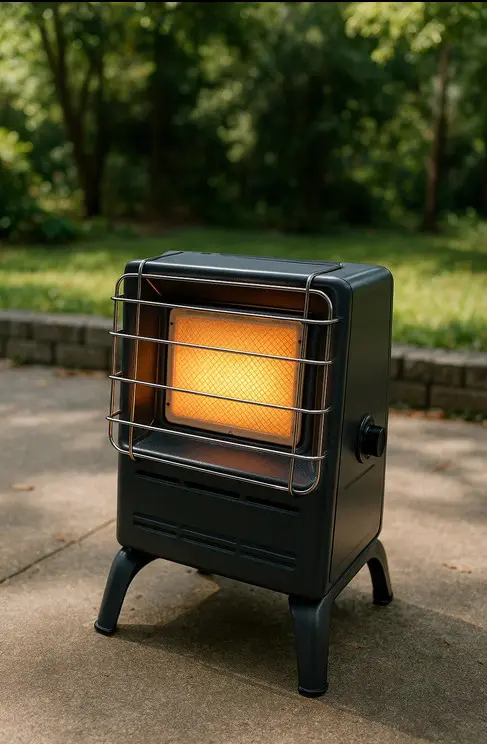
Electric patio heaters typically use infrared heating elements that convert electrical energy directly into radiant heat. The heat is then transferred to surrounding objects and people, rather than warming the air. This results in a more targeted heating effect, which can be useful in windy conditions. Gas patio heaters, on the other hand, generally use propane or natural gas as a fuel source. Combustion generates heat, which is radiated through a reflector to provide warmth to the surrounding area. Their design often includes larger bodies and visible flames, which create a traditional outdoor heating ambiance. Both systems differ significantly in construction, leading to variations in portability, aesthetics, and heating coverage.
| Feature | Electric Patio Heater | Gas Patio Heater |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Infrared element | Propane/Natural gas combustion |
| Visual Effect | Subtle, glowing rods | Visible flame |
| Size & Form | Slim, wall/ceiling/freestanding | Taller, bulky with base |
| Noise Level | Silent | Slight combustion noise |
Heating Performance and Coverage
Heating performance is one of the primary considerations when comparing electric and gas heaters. Electric patio heaters provide direct radiant heat, which is effective for spot heating and smaller areas. They are often better suited for enclosed or semi-enclosed spaces where heat retention is higher. Gas patio heaters, in contrast, can generate more powerful heat, making them suitable for larger open-air areas such as spacious patios, outdoor dining areas, or event spaces. However, gas heaters may be less efficient in windy environments since heated air can disperse quickly. The choice between them often depends on whether the user requires focused heating or wide coverage.

Energy Efficiency and Running Costs
When it comes to efficiency, electric patio heaters are known for converting almost all input energy into usable heat, with minimal energy loss. However, electricity costs can vary depending on local rates, which influences long-term expenses. Gas patio heaters, although less efficient in direct conversion, can sometimes offer lower running costs depending on fuel prices and availability. Propane heaters, for instance, may be more expensive to operate compared to natural gas heaters, but they offer portability. The decision on efficiency and cost-effectiveness depends not only on the technical efficiency but also on local utility costs and expected usage patterns.
Installation and Portability
Installation requirements differ considerably between electric and gas heaters. Electric patio heaters usually require only an accessible power outlet and can be wall-mounted, ceiling-mounted, or freestanding. They are relatively simple to install and do not require extensive infrastructure. Gas patio heaters, particularly those running on natural gas, may need professional installation, including gas line connections. Portable propane gas heaters offer flexibility but require periodic cylinder replacement. While electric heaters are generally lighter and easier to move, gas heaters tend to be bulkier but may provide more independent operation without relying on electrical outlets.
| Aspect | Electric Patio Heater | Gas Patio Heater |
|---|---|---|
| Setup Complexity | Plug-and-play | May require professional gas line |
| Portability | Lightweight, easy to move | Heavy, propane tanks add bulk |
| Placement Options | Wall, ceiling, floor | Freestanding, fixed |
| Independence | Needs outlet | Works without electricity |
Safety Considerations
Safety is an important factor in selecting a patio heater. Electric heaters eliminate the risks associated with combustion, such as carbon monoxide emissions, making them safer for enclosed spaces. They are also less prone to tipping hazards because many models are compact and wall-mounted. Gas patio heaters, however, must be used with caution, especially in enclosed areas, due to potential fire hazards and emissions. Proper ventilation is essential when using gas heaters. In addition, handling propane tanks requires care to prevent leaks. Overall, electric heaters may provide a safer option for indoor-adjacent use, while gas heaters are better suited for open-air areas with proper safety precautions.
 |
 |
Environmental Impact
Environmental considerations also play a role in choosing between the two systems. Electric patio heaters produce no direct emissions at the point of use, making them environmentally cleaner in terms of local air quality. Their overall environmental impact depends on how the electricity is generated—renewable sources make them a greener option, while fossil-fuel-based electricity reduces the benefit. Gas patio heaters release carbon dioxide and water vapor during operation, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Although they provide powerful heating, their environmental footprint is generally higher compared to electric heaters.
Cost Comparison: Purchase and Maintenance
The cost of patio heaters is not limited to the purchase price; ongoing maintenance and fuel or energy costs also matter. Electric heaters usually have lower upfront costs and minimal maintenance needs. Their components are relatively durable, and servicing requirements are low. Gas patio heaters may have higher initial costs, especially for larger models or built-in systems. They also require regular checks of burners, gas lines, and fuel supplies. Over time, the total cost of ownership depends on both usage frequency and local energy prices.
Below is a simplified cost comparison table:
|
Aspect |
Electric Patio Heater |
Gas Patio Heater |
|
Initial Purchase Cost |
Generally lower |
Generally higher |
|
Running Costs |
Depends on electricity rates |
Depends on propane/natural gas prices |
|
Maintenance |
Low, minimal servicing required |
Moderate, requires gas system checks |
|
Lifespan |
Long with minimal wear |
Long but dependent on combustion parts |
Application Scenarios
Electric patio heaters are commonly used in homes, cafés with small terraces, and semi-enclosed areas where direct and quiet heating is required. Their compactness and silent operation make them appealing for urban and residential settings. Gas patio heaters, on the other hand, are widely used in outdoor restaurants, large patios, and public venues where powerful heating is necessary to cover wide spaces. Their flame presence also adds an aesthetic atmosphere, making them popular for hospitality applications. The decision largely depends on the environment, required heating intensity, and user preferences.
Comparative Summary Table
|
Criteria |
Electric Patio Heater |
Gas Patio Heater |
|
Heating Method |
Infrared radiant heating |
Combustion heat with flame |
|
Heat Coverage |
Localized, effective in small areas |
Wide coverage, suitable for open spaces |
|
Energy Efficiency |
High (almost full conversion) |
Moderate, with energy loss |
|
Safety |
High, no emissions |
Requires ventilation and fire safety |
|
Environmental Impact |
Cleaner at point of use |
Produces CO₂ emissions |
|
Installation |
Simple, needs power outlet |
More complex, may need gas lines |
|
Portability |
Easy to move, lightweight |
Portable with propane, heavier design |

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Français
Français Español
Español Language
Language 










